The site is read-only. Please transition to use Robotics Stack Exchange
| ROS Resources: Documentation | Support | Discussion Forum | Index | Service Status | ros @ Robotics Stack Exchange |
 | 1 | initial version |
(Hopefully) you shouldn't need to implement your own force-torque sensor for Sawyer in Gazebo. The sawyer_gazebo package actually simulates the torque values being experienced by each joint in the arm directly. You can see each of these torques on the topic /robot/joint_states. A force-torque sensor is usually used to measure the force experienced at the end effector of the robot. Part of the simulation is a handy topic that reports all of these joint torques trasnformed into the endpoint frame on the /robot/limb/right/endpoint_state topic using the intera_core_msgs/EndpointState message.
The following is the RViz rendering of the effort portion of the /robot/joint_states topic:
C:\fakepath\sawyer_torques_in_gazebo.png
 | 2 | No.2 Revision |
(Hopefully) you shouldn't need to implement your own force-torque sensor for Sawyer in Gazebo. The sawyer_gazebo package actually simulates the torque values being experienced by each joint in the arm directly. You can see each of these torques on the topic /robot/joint_states. A force-torque sensor is usually used to measure the force experienced at the end effector of the robot. Part of the simulation is a handy topic that reports all of these joint torques trasnformed into the endpoint frame on the /robot/limb/right/endpoint_state topic using the intera_core_msgs/EndpointState message.
The following is the RViz rendering of the effort portion of the /robot/joint_states topic:
C:\fakepath\sawyer_torques_in_gazebo.png](/upfiles/15216420697813004.png)
 | 3 | No.3 Revision |
(Hopefully) you shouldn't need to implement your own force-torque sensor for Sawyer in Gazebo. The sawyer_gazebo package actually simulates the torque values being experienced by each joint in the arm directly. You can see each of these torques on the topic /robot/joint_states. A force-torque sensor is usually used to measure the force experienced at the end effector of the robot. Part of the simulation is a handy topic that reports all of these joint torques trasnformed into the endpoint frame on the /robot/limb/right/endpoint_state topic using the intera_core_msgs/EndpointState message.
The following is the RViz rendering of the effort portion of the /robot/joint_states topic:
C:\fakepath\sawyer_torques_in_gazebo.png](/upfiles/15216420697813004.png)]
 | 4 | No.4 Revision |
(Hopefully) you shouldn't need to implement your own force-torque sensor for Sawyer in Gazebo. The sawyer_gazebo package actually simulates the torque values being experienced by each joint in the arm directly. You can see each of these torques on the topic /robot/joint_states. A force-torque sensor is usually used to measure the force experienced at the end effector of the robot. Part of the simulation is a handy topic that reports all of these joint torques trasnformed into the endpoint frame on the /robot/limb/right/endpoint_state topic using the intera_core_msgs/EndpointState message.
The following is the RViz rendering of the effort portion of the /robot/joint_states topic:
C:\fakepath\sawyer_torques_in_gazebo.png]
 | 5 | No.5 Revision |
(Hopefully) you shouldn't need to implement your own force-torque sensor for Sawyer in Gazebo. The sawyer_gazebo package actually simulates the torque values being experienced by each joint in the arm directly. You can see each of these torques on the topic /robot/joint_states. A force-torque sensor is usually used to measure the force experienced at the end effector of the robot. Part of the simulation is a handy topic that reports all of these joint torques trasnformed into the endpoint frame on the /robot/limb/right/endpoint_state topic using the intera_core_msgs/EndpointState message.
The following is the RViz rendering of the effort portion of the /robot/joint_states topic:
C:\fakepath\sawyer_torques_in_gazebo.pngSawyer RViz Torques in Gazebo
 | 6 | No.6 Revision |
(Hopefully) you shouldn't need to implement your own force-torque sensor for Sawyer in Gazebo. The sawyer_gazebo package actually simulates the torque values being experienced by each joint in the arm directly. You can see each of these torques on the topic /robot/joint_states. A force-torque sensor is usually used to measure the force experienced at the end effector of the robot. Part of the simulation is a handy topic that reports all of these joint torques trasnformed into the endpoint frame on the /robot/limb/right/endpoint_state topic using the intera_core_msgs/EndpointState message.
The following is the RViz rendering of the effort portion of the /robot/joint_states topic:
Sawyer RViz Torques in Gazebo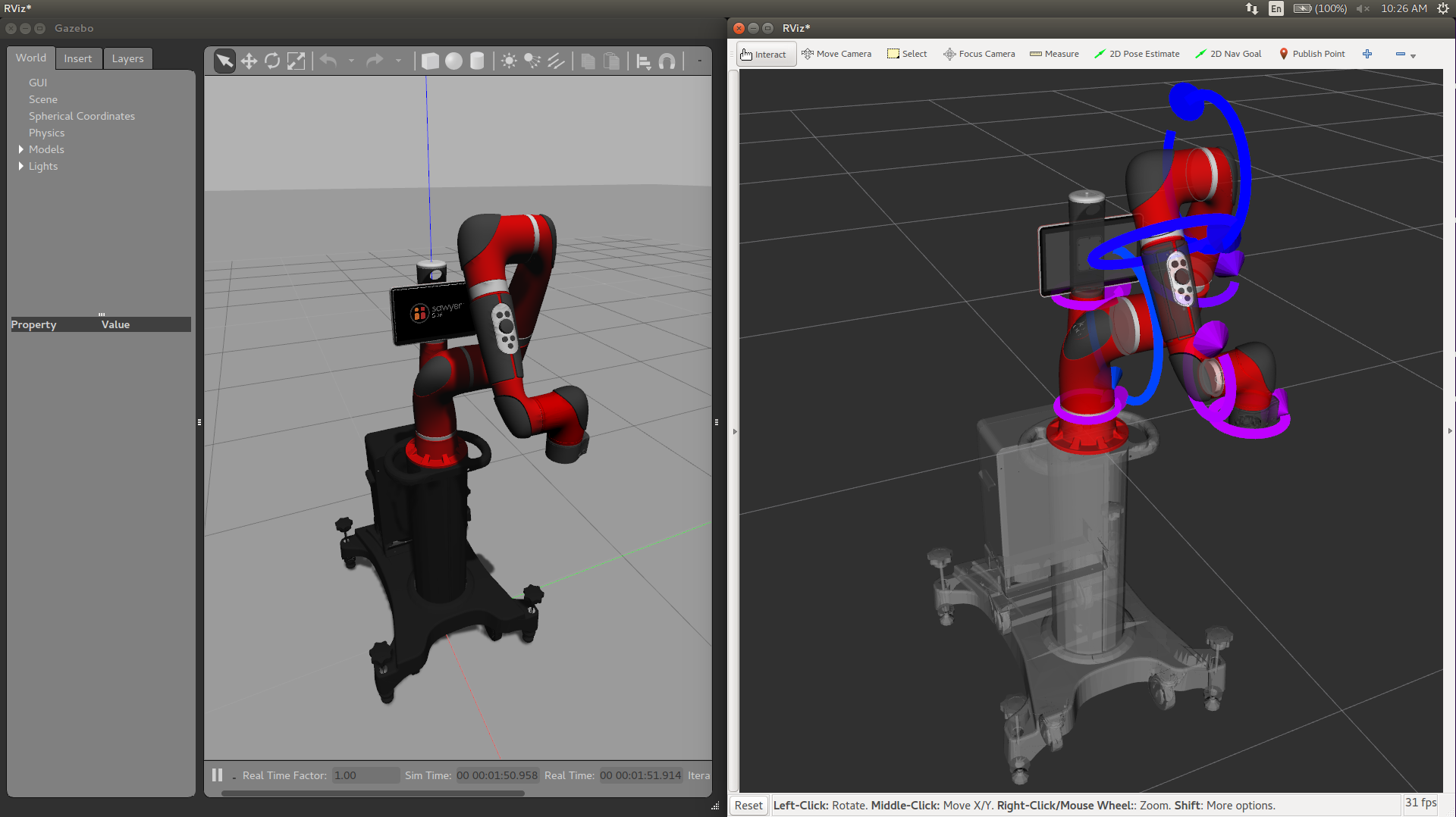
 | 7 | No.7 Revision |
(Hopefully) you shouldn't need to implement your own force-torque sensor for Sawyer in Gazebo. The sawyer_gazebo package actually simulates the torque values being experienced by each joint in the arm directly. You can see each of these torques on the topic /robot/joint_states. A force-torque sensor is usually used to measure the force experienced at the end effector of the robot. Part of the simulation is a handy topic that reports all of these joint torques trasnformed are transformed into the endpoint frame on the /robot/limb/right/endpoint_state topic using the intera_core_msgs/EndpointState message.
The following is the RViz rendering of the effort portion of the /robot/joint_states topic:

 ROS Answers is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 license.
ROS Answers is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 license.